What is ZTNA? Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is the modern enterprise standard for secure access control, especially as cloud, remote work and edge computing trends turn the security perimeter inside out. Traditional network access controls simply can’t stand up to the ever-evolving cyberthreat landscape. In this blog, we review how you can implement the operational efficiencies, convenience and agility of ZTNA security within your organization to support your larger Zero Trust strategy.
Zero Trust Security Journey
Zero Trust security, in the broadest sense, is based on the fundamental idea that no user—human or machine—should be automatically granted access to anything within your network. This may seem extreme, but this “least privilege” approach significantly improves your overall security posture.
Wikipedia describes it as, “The zero trust security model (also, zero trust architecture, zero trust network architecture, ZTA, ZTNA), sometimes known as perimeterless security, describes an approach to the design and implementation of IT systems. The main concept behind the zero trust security model is "never trust, always verify,” which means that devices should not be trusted by default, even if they are connected to a permissioned network such as a corporate LAN and even if they were previously verified.”
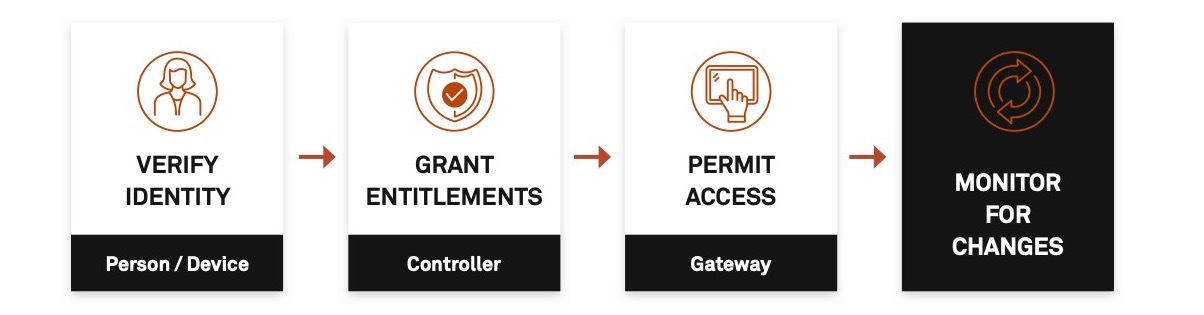
With ZTNA security, users are denied access to digital assets by default. Once identity is verified (user + device + context), access is permitted based on dynamic policies and entitlements. Individual privileges are conditional and contextual and can be expanded or restricted based on activities continuously monitored by the ZTNA solution. This gives your business the ability to immediately stop suspicious behavior before it causes harm.
Zero Trust security also significantly decreases the attack surface by completely cloaking your company’s resources … making them invisible to bad actors. This provides another layer of protection by ensuring only authenticated users can see your resources.
The Zero Trust security model is often referred to in alignment with Software-Defined Perimeter (SDP) solutions and you’ll find these names used interchangeably in the Zero Trust space.
Benefits of ZTNA Security
By implementing Zero Trust security, organizations can:
- Simplify and strengthen network access controls
- Reduce attack surface area
- Streamline policy management administration
- Improve end-user experience
- Unleash digital transformation with integrations and automation
ZTNA Compared to Other Access Control Solutions
ZTNA security is different from other legacy offerings such as:
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
- Network Access Control (NAC)
- Local Area Networks (LANs)
The most significant difference between legacy solutions and ZTNA security is their use of a “default allow” vs. ZTNA's inherent “default deny” posture. Many VPN, NAC and LAN offerings allow access if a user meets defined policy requirements. From there, access by a user—or malicious actor—is only limited by other controls, making it easy to move laterally between networks. Implementing ZTNA security significantly mitigates this risk.
Implementing Zero Trust security does not involve completely ripping and replacing legacy technologies. ZTNA can work alongside your existing security architecture to improve your overall security posture.
Firewalls are another common legacy security solution. ZTNA security solutions do not replace firewalls, but work with them to make them more agile. Certainly, firewalls are regularly relied on, yet are relatively stagnant and hard to modify once set up. There are plenty of reasons why firewall modifications might be needed, but it is very difficult to make changes to access rules. ZTNA removes this challenge by overlaying more easily managed security.
Quick Guide to ZTNA Security Implementation
ZTNA Architectural Models
There are two main ZTNA architectural methods, each with pros and cons. It is essential to consider these differences as they will directly impact which solutions will or won’t work for you.
- Client-based: This architecture installs a client on a server or user device and the endpoint initiates the connection process. This setup makes it easy to apply Zero Trust to all resources (including custom and legacy applications) and enhances device posture checking. However, there are some instances in which a client can’t be installed, such as when trying to get access from an unmanaged device. This can create issues, especially if you often must set up third-party or contractor access.
- Browser-based: In this “clientless” approach, the application or service initiates the connection and the user connects using an Internet browser. This gets around the unmanaged device issue with the client-based architecture and is best for one-off use cases or smaller, less complex applications. It’s important to note this architecture only supports web-based applications and protocols, which poses some significant limitations.
Some ZTNA security solutions offer a hybrid choice so you can take advantage of both models. This can be ideal for organizations looking to go clientless for third-party access, but still use a client for legacy applications.
When embarking on your ZTNA journey, consider your current IT stack as that will have a direct impact on which architectural approach will work best for your organization and, in turn, which ZTNA security operations you’ll have.
Ensuring ZTNA Security Success: How to Select the Right Zero Trust Security Solution
Picking the right ZTNA security solution is key to ensuring a successful Zero Trust journey. When evaluating ZTNA security vendors, here are questions to think about:
- How will multiple, disparate identity providers be managed?
- What is your Zero Trust roadmap?
- Where do your resources reside?
- Do you require hosting yourself or deploying as-a-service?
- What is the flow of network traffic?
- What types of applications need to be integrated?
You also must consider how you will:
- Avoid exposing ports and hidden infrastructure
- Deal with device and user risks
- Manage “up rules” vs. “down rules” device policies
- Integrate into the broader security ecosystem
- Continue to scale as the business grows
Success Starts with the Right Zero Trust Security Solution
Your Zero Trust journey starts with finding the right solution to fit your organization’s unique needs. Appgate SDP is an industry-leading, enterprise-grade scalable and customizable ZTNA security platform. Known for its ability to simplify configuration, operations, management and compliance, Appgate SDP delivers Zero Trust security to improve network access control management across your remote workforce.
To learn more, get direct access to the ZTNA Everything You Need to Know eBook.
Want to see how Appgate SDP can support your Zero Trust security strategy? Schedule a demo.
